Project managers often face a daunting challenge: keeping track of multiple projects simultaneously. As each project tends to operate with its own set of technologies and software tools, communication becomes fragmented and essential information is scattered across various platforms.
However, there’s a solution on the horizon: interoperability. This principle serves as a unifying force, enabling smooth integration and communication between disparate systems and tools, ultimately easing the burden on project managers and enhancing overall efficiency.
In this comprehensive guide, we explain how interoperability works, its levels, benefits and diverse use cases across industries. Additionally, we explore how PM3, the award-winning PPM tool by BestOutcome, can help your organisation achieve interoperability.

Interoperability refers to the ability of different systems, applications, or tools to exchange and interpret data.
It enables organisations to bridge the gap between different technologies, facilitating smooth communication, data sharing and collaboration.
When it comes to Project Portfolio Management (PPM), interoperability ensures that project management tools, systems and processes can effectively interact and integrate with each other, minimising silos and maximising productivity.
Interoperability operates on four levels, each contributing to the integration of systems and processes within an organisation.
At the foundational level, interoperability ensures the basic connectivity between different systems and tools. It establishes the infrastructure necessary for data exchange to occur, laying the groundwork for more advanced forms of integration.
Think of it as the building blocks upon which interoperability is built, forming the essential framework for communication and interaction.
Structural interoperability focuses on the format and structure of exchanged data. It involves standardising data formats, protocols and interfaces to ensure compatibility between systems.
By establishing common data schemas and protocols, structural interoperability enables seamless data exchange without the need for extensive conversion or translation processes.
This level ensures that data can be accurately interpreted and utilised by receiving systems, regardless of their underlying technologies.
Semantic interoperability takes integration a step further by addressing the meaning and interpretation of exchanged data. It involves establishing shared vocabularies, ontologies and data semantics to facilitate mutual understanding between systems.
This level ensures that data exchanged between different systems retains its intended meaning and context, enabling more meaningful and insightful interactions.
Semantic interoperability is essential for enabling advanced functionalities such as data analytics, decision support and knowledge sharing across disparate systems.
Beyond technical considerations, organisational interoperability focuses on aligning business processes, policies and strategies to support seamless integration.
It involves coordinating workflows, roles and responsibilities across departments and stakeholders to ensure cohesive operations.
Organisational interoperability is crucial for overcoming cultural barriers, organisational silos and resistance to change, fostering a collaborative environment conducive to effective integration.
By aligning business objectives and priorities, organisational interoperability enables organisations to leverage interoperability to achieve strategic goals and objectives.
Interoperability functions through a series of mechanisms and practices designed to facilitate communication and integration between different systems, applications and processes.
One of the fundamental aspects of interoperability is the use of standardised protocols and data formats.
These protocols establish a common language for communication between systems, ensuring that data can be exchanged and interpreted accurately.
Similarly, standardised data formats enable consistent representation and interpretation of information across disparate systems, minimising compatibility issues and facilitating smooth data exchange.
APIs play a crucial role in enabling interoperability by providing a standardised interface for interaction between software components.
APIs define the methods and protocols through which different systems can communicate and exchange data, allowing developers to integrate functionality seamlessly.
By exposing specific endpoints and functionalities, APIs enable systems to interact with each other in a controlled and predictable manner, simplifying integration efforts and reducing development time.
Middleware and integration platforms serve as intermediaries between different systems, facilitating communication and data exchange.
These platforms provide a centralised hub for integrating disparate applications, databases and services, enabling seamless interoperability across heterogeneous environments.
By abstracting the complexities of integration and providing pre-built connectors and adapters, middleware and integration platforms streamline the process of connecting and orchestrating interactions between systems.
In many cases, data exchanged between different systems may need to be transformed or mapped to ensure compatibility and consistency.
Data mapping involves converting data from one format to another, aligning it with the requirements of the receiving system.
Transformation processes may include data cleansing, validation and enrichment to ensure that exchanged data is accurate, complete and compliant with relevant standards.
By implementing robust data mapping and transformation techniques, organisations can overcome data interoperability challenges and ensure seamless integration between systems.
Security and governance are paramount considerations in ensuring the reliability and integrity of interoperability mechanisms.
Secure communication protocols, encryption techniques and access controls help protect sensitive data from unauthorised access and ensure confidentiality and integrity during data exchange.
Additionally, governance frameworks and standards establish guidelines and policies for managing interoperability efforts, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and industry best practices.
Interoperability offers a wide range of benefits to organisations across various industries, enhancing efficiency, collaboration and innovation. Here are some of the key benefits:
By enabling seamless communication and integration between different systems and processes, interoperability streamlines workflows and reduces manual intervention.
This leads to increased productivity as employees spend less time navigating between disparate systems and can focus more on value-added tasks.
Did you know that one in five employees waste one third of their working day on unproductive tasks? Find out how timesheet analysis can help your organisation improve productivity.
Interoperability provides access to a wealth of integrated data from across the organisation, enabling better-informed decision making.
With real-time access to relevant information and insights, decision makers can reach faster, more accurate decisions that are based on a comprehensive understanding of the business landscape.
By eliminating data silos and redundant processes, interoperability helps organisations streamline operations and reduce overhead costs.
Integrated systems require fewer resources to manage and maintain, leading to cost savings in terms of infrastructure, maintenance and support.
Interoperability enables organisations to adapt quickly to changing business requirements and market conditions.
Integrated systems can be easily reconfigured and scaled to accommodate evolving needs, allowing organisations to respond rapidly to new opportunities and challenges.
Interoperability fosters collaboration among different departments, teams and stakeholders by providing a common platform for communication and data sharing.
Integrated systems facilitate seamless collaboration, enabling teams to work together more effectively towards common goals.
Breaking down barriers between different systems and processes, interoperability promotes innovation by facilitating the exchange of ideas, information and best practices.
Integrated systems provide a fertile ground for experimentation and exploration, driving continuous improvement and innovation within the organisation.

Interoperability finds widespread application across diverse industries, revolutionising operations and driving efficiency. Let’s explore some key use cases across various sectors:
In the healthcare industry, interoperability enables seamless exchange of patient data between different healthcare systems and providers.
This facilitates continuity of care, improves patient outcomes and enhances clinical decision-making.
For example, interoperable electronic health records (EHR) systems allow healthcare professionals to access patient information quickly and securely, regardless of their location or the system they use.
Interoperability plays a crucial role in government operations, enabling different agencies and departments to share information and collaborate effectively.
Integrated government systems streamline administrative processes, improve service delivery, and enhance citizen engagement.
For instance, interoperable systems enable smooth data exchange between tax authorities, social services and law enforcement agencies, facilitating faster and more efficient public service delivery.
In the realm of public safety, interoperability ensures seamless communication and coordination among emergency response agencies, such as police, fire departments and emergency medical services.
Integrated public safety systems enable real-time sharing of critical information, improving situational awareness and response times during emergencies.
For example, interoperable communication systems allow first responders to coordinate their efforts and resources effectively, enhancing public safety and saving lives.
Interoperability is essential in software engineering, enabling different software components and systems to work together seamlessly.
Integrated development environments (IDEs), application programming interfaces (APIs), and software development kits (SDKs) facilitate interoperability between different programming languages, platforms and frameworks.
This allows developers to build and integrate software solutions more efficiently, accelerating the development process and improving software quality.
In the military domain, interoperability is critical for ensuring seamless communication and collaboration among different branches of the armed forces and allied nations.
Integrated military systems enable interoperable command and control, intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance (C4ISR) capabilities, enhancing military effectiveness and operational efficiency.
For example, interoperable communication systems allow military units to exchange tactical information and coordinate joint operations in real time, improving mission success and force effectiveness.
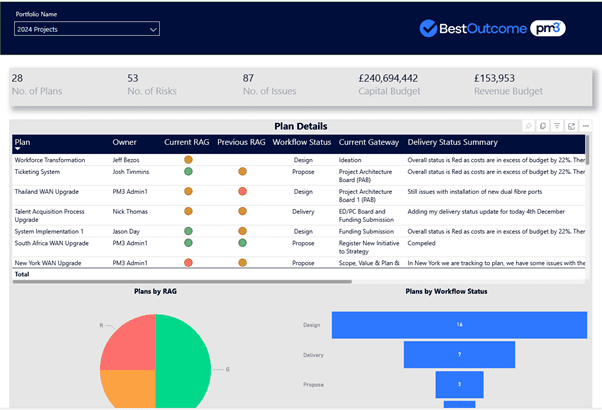
As organisations aim for efficient project and portfolio management (PPM), seamless integration and collaboration across various systems and tools become crucial.
As highlighted in the preceding sections, interoperability plays a central role in driving innovation and efficiency in modern organisations.
One tool that can enable you to achieve interoperability is PM3 – a sophisticated software solution designed by BestOutcome to streamline project and portfolio management processes, ensuring clarity and results every step of the way.
Here’s how PM3 facilitates interoperability:
PM3 offers seamless integration with other systems and tools, enabling organisations to connect and exchange data effortlessly.
Whether it’s integrating with existing enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, customer relationship management (CRM) software, or third-party project management tools, PM3 ensures compatibility and interoperability across the organisation’s technology stack.
This seamless integration streamlines data exchange, enhances collaboration and improves overall efficiency.
PM3 adheres to standardised data formats and protocols, ensuring compatibility and consistency in data exchange.
Whether importing project data from external sources or exporting reports to other systems, PM3 ensures that data is represented in a standardised format that can be easily interpreted and utilised by other systems.
This standardised approach to data exchange facilitates interoperability and eliminates compatibility issues, enabling smooth communication and collaboration between different systems and stakeholders.
PM3 provides robust APIs and middleware that facilitate seamless integration with other systems and applications.
These APIs allow organisations to extend PM3’s functionality, automate workflows and integrate with third party tools and services.
By providing a standardised interface for communication and data exchange, PM3 APIs enable interoperability between PM3 and other systems, empowering organisations to leverage PM3’s capabilities within their existing technology ecosystem.
PM3 fosters a collaborative environment where teams can work together seamlessly, regardless of their location or the tools they use.
PM3’s intuitive interface and collaborative features enable teams to share project information, collaborate on tasks and communicate effectively in real time.
Whether through the PM3 web interface or the dedicated PM3Team mobile app, PM3 provides a unified platform for collaboration that promotes interoperability and enhances team productivity.
PM3 aligns with industry standards and best practices, ensuring compatibility and interoperability with other PPM tools and systems.
Whether following traditional project management methodologies like PRINCE2™ or agile practices such as Scrum, PM3 provides the necessary tools and functionalities to support diverse project management frameworks.
This alignment with industry standards facilitates interoperability and enables organisations to seamlessly integrate PM3 into their existing project management processes and workflows.

Our products help you deliver successful change programmes and projects by always focusing on the overall business outcomes. Find out how our products can help you.
Choosing a PPM Tool can be a fraught and challenging process. Getting it right requires forethought,...
Read more >It is critical that you take steps to select the right PPM tool as the wrong choice can have a negat...
Read more >Listen to David’s 20 minute segment with host Stephanie Smith where he discusses PPM tools in the ...
Read more >